At Virtrigo, we prioritize transparency and honesty in all our interactions. As part of our commitment to providing exceptional service, we want to clarify certain limitations of liability that apply to our website and services.
The way Indian businesses handle personal data is undergoing a major transformation. With the enactment of the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 (DPDP Act), India has introduced its first comprehensive data privacy law. If your business collects, processes, or stores personal data digitally, compliance with the DPDP Act is now a legal requirement.
This guide breaks down the essentials of the DPDP Act—what it is, who it applies to, the key provisions, penalties, and most importantly, how your business can stay compliant.
What is the DPDP Act 2023?
Passed in August 2023, the DPDP Act regulates the collection, processing, and storage of digital personal data in India. Modeled in part after the EU’s GDPR, it addresses the growing need for privacy in the country’s digital ecosystem.
Key Highlights:
Who Must Comply with the DPDP Act?
Any organization that processes digital personal data falls under the category of Data Fiduciary.
Entities Required to Comply:
Significant Data Fiduciaries (SDFs):
Organizations dealing with large volumes or sensitive data have additional responsibilities:
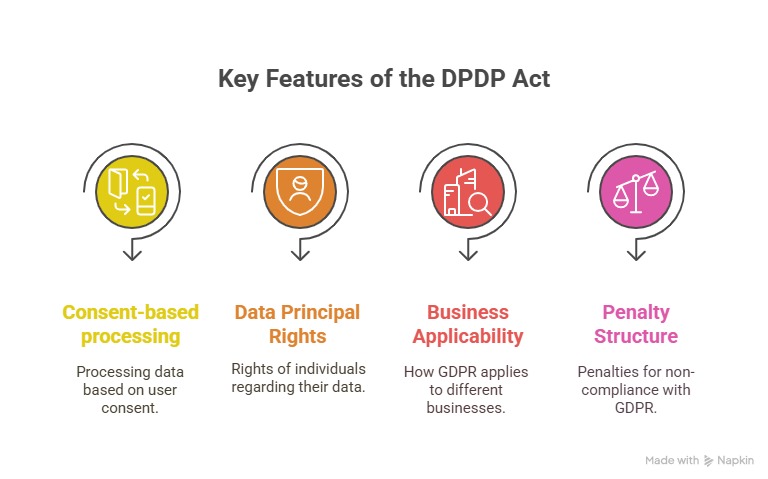
Key Provisions Under the DPDP Act
Manage Consent the Right Way
Know the Rights of Data Principals
Understand Your Duties as a Data Fiduciary
DPDP vs GDPR: A Clear Comparison for Indian Companies
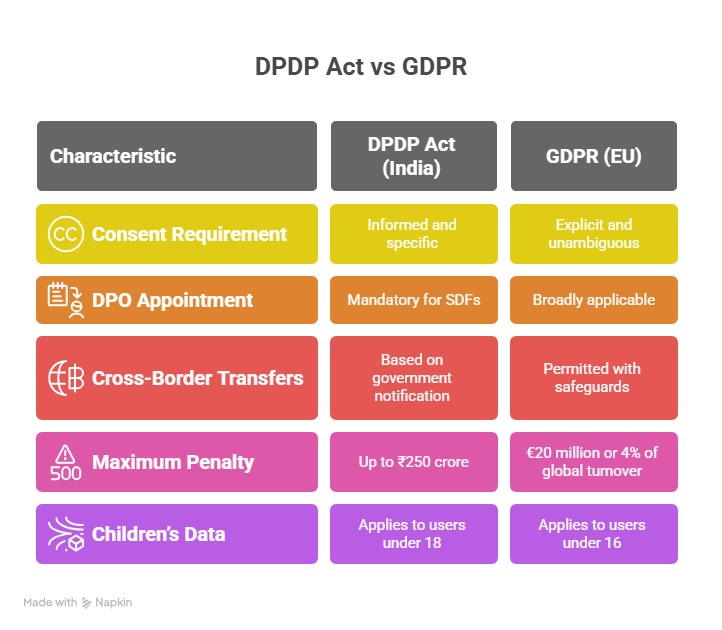
Although inspired by the GDPR, the DPDP Act includes several India-specific provisions that businesses must understand.
How to Ensure DPDP Compliance: A Step-by-Step Business Guide

Sector-Wise Impact of the DPDP Act: IT, SaaS, Startups & More
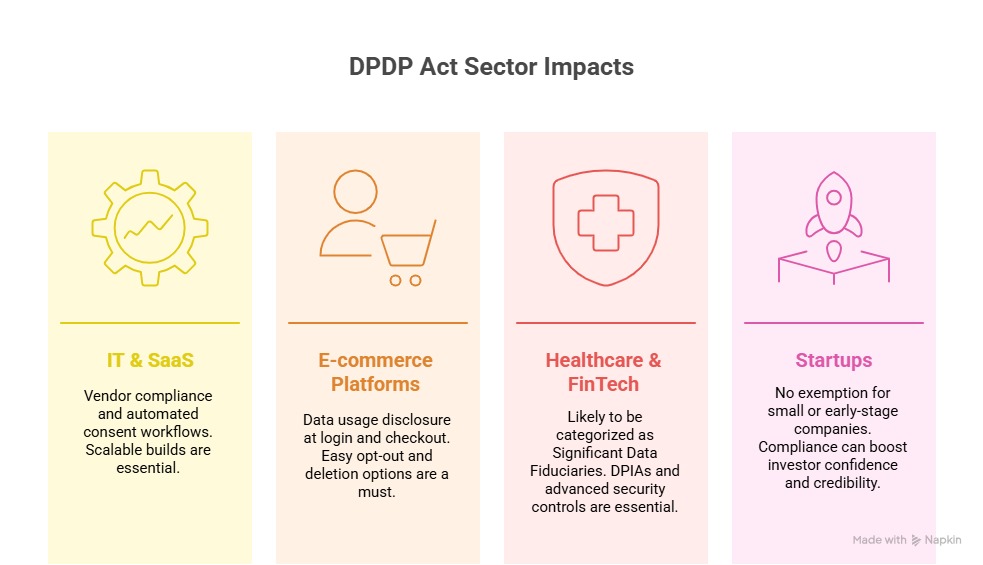
For IT & SaaS Companies
For E-commerce Platforms
For Healthcare & FinTech
For Startups
Penalties for Non-Compliance Are High
Violating the DPDP Act can lead to heavy fines:
The Data Protection Board of India is authorized to investigate, conduct hearings, and impose these penalties.
Your Roadmap to DPDP Readiness Starts Now
Following the DPDP Act isn’t just about avoiding penalties—it’s about building consumer trust and future-proofing your business.
Here’s what you can do:
Let Us Help You Get DPDP Compliant
We assist businesses in navigating India’s data privacy laws with:
📥 Discover more about the DPDP Compliance Checklist right now!
Contact us at support@virtrigo.com to book your consultation and protect your business from data risks.
Sign up to receive notifications about the latest news and events from us!
1-7-132/A, SRK Nagar Rd, Harinagar, Musheerabad, Zamistanpur, Hyderabad, Telangana 500020, India.
Call us: +91 80960 41070
Mail: support@virtrigo.com
Mon – Sat: 8.00am – 18.00pm / Holiday : Closed
